Camming and Gearing Functions
Use camming and gearing motion to synchronize one or more follower axes to a leader axis. The motion of the follower axes is a function of the motion of the leader axis.
Limitations
Camming and gearing motion does not apply to the acceleration limiting feature, the feedrate limiting feature, and the automatic acceleration feature.
The conditions that follow automatically stop the relation between the follower axis and the leader axis:
- If you use the CammingOff() function or the GearingOff() function on the follower axis.
- If you use the Abort() function on the leader axis or the follower axis.
- If you disable the follower axis.
- If software clamping occurs on the follower axis.
- If the controller generates an axis fault on the follower axis and that fault is set in the FaultMaskDisable Parameter or the FaultMaskDecel Parameter.
You cannot configure a camming or gearing relation between axes that have different position update rates. The table that follows shows the position update rates for each drive type.
| Drive Type | Position Update Rate | |
|---|---|---|
| Servo Axis | FLEX, iHXA4, HXA4, iXA4, and XA4 | 10 kHz |
| All others | 20 kHz | |
| Galvo Axis | 100 kHz | |
Camming Motion
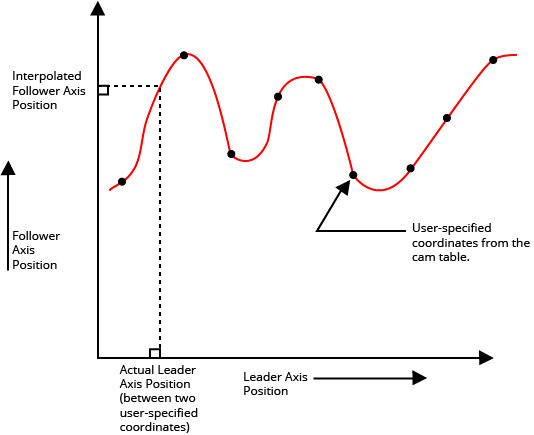
Camming motion causes the position or velocity of a follower axis to move based on the position of the leader axis and the coordinates that you specify in a cam table.
IMPORTANT: The ReverseMotionDirection Parameter can have an effect on the direction of motion for the leader or follower axes if you specify CammingUnits in counts.
For an example program, refer to the Camming example program.
Loading a Cam Table
The CammingLoadTableFromArray() function lets you load a cam table, which includes the coordinates that specify the follower axis position for each leader axis position.
You can specify leader axis and follower axis positions with user units or counts. The unit type that you use depends on the value of the $unitsMode argument that you specify to the CammingLoadTableFromArray() function. Set this argument with enum CammingUnits.
Use the $interpolationMode argument of the CammingLoadTableFromArray() function to configure the type of interpolation that the controller uses when the position of the leader axis is different from one of the positions specified in the $leaderValues argument:
- If the leader axis position on the controller is equal to one of the positions specified in the $leaderValues argument, the controller uses the value of that cam table entry as the follower axis position.
- If the leader axis position on the controller is between two of the leader axis positions in the cam table, the controller uses the specified linear or cubic spline interpolation to calculate a follower axis position that is between the two corresponding follower axis positions in the table.
Set the $interpolationMode argument with enum CammingInterpolation.
Tip: Aerotech recommends that you use cubic spline interpolation to get maximum smoothness for the motion of the follower axis. But if you want minimum rippling to occur, use linear interpolation.
Use the $wrapMode argument of the CammingLoadTableFromArray() function to configure the behavior of the camming motion when the leader axis is out of the range of positions that you specify for the $leaderValues argument. The wrapping modes are as follows:
- If you specify that wrapping must not occur: The controller uses the value of the $leaderValues argument that is nearest to the position of the leader axis to determine the position of the follower axis.
- If you specify that wrapping must occur: The controller wraps the position value of the leader axis to determine the position of the follower axis.
Set the $wrapMode argument with enum CammingWrapping.
Use the $tableOffset argument of the CammingLoadTableFromArray() function to offset the position value of the leader axis that is used to determine the position of the follower axis. For this argument, you can specify the types of values that follow:
- If you specify a value of zero, no offset occurs.
- If you specify a positive value, the cam table shifts to the left by the quantity of the offset that you specify.
- If you specify a negative value, the cam table shifts to the right by the quantity of the offset that you specify.
Loads a camming table into the SMC.
Arguments
$tableNum The camming table number to use. This value must be greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 99. Use this number when using the CammingOn() and CammingFreeTable() functions.
$leaderValues Array of leader axis position values for the follower axis to track.
$followerValues Array of follower axis positions or velocities to use.
$numValues The number of values in the leaderValues and followerValues arrays.
$unitsMode The units of the values in the camming table.
$interpolationMode The interpolation type to use if the position of the leader axis is between two values in the table.
$wrapMode Determines how a leader axis position value outside of the table is treated.
$tableOffset An offset applied to all follower axis position or velocity values in the table.
| enum CammingUnits
Primary = 0 Secondary = 1 Counts = 2 end |
| enum CammingInterpolation
Linear = 0 Cubic = 1 end |
| enum CammingWrapping
NoWrap = 0 Wrap = 1 end |
Enabling and Disabling Camming
IMPORTANT: Before you enable or disable cam table motion, make sure that the leader axis is stationary.
The CammingOn() function synchronizes the follower axis to the leader axis.
The CammingOff() function stopz synchronizing the follower axis to the leader axis.
Use the $source argument of the CammingOn() function to configure the position value of the leader axis that is used to determine the position of the follower axis. Set this argument with enum CammingSource.
Use the $output argument of the CammingOn() function to configure the type of output that camming motion generates for the follower axis. You can set the $output argument with enum CammingOutput. Specify one of the output modes that follow:
- Relative Output mode causes the controller to continuously position the follower axis at the difference between the position of the follower axis when the camming motion was enabled and the position of the follower axis that is generated from the cam table.
- Absolute Output mode causes the controller to automatically generate MoveRapid() motion that moves the follower axis to the correct position before the camming motion starts. This position is generated from the cam table.
- Velocity Output mode causes the controller to use the positions specified for the follower axis as velocities. These positions are specified in the CammingLoadTableFromArray() function and are always specified in units/millisecond.
The MaxSpeedClamp Parameter does not limit the velocity of follower axes during camming motion.
To release a cam table from the controller, use the CammingFreeTable() function.
Enables camming on the specified leader axis and follower axis.
Arguments
$followerAxis The axis to set as the follower axis.
$leaderAxis The axis to set as the leader axis.
$tableNum The camming table number to use. This value must be greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 99.
$source The signal on the leader axis that the follower axis will track.
$output The output signal to generate and the synchronization mode to use on the camming follower axis.
| enum CammingSource
PositionFeedback = 0 PositionCommand = 1 AuxiliaryFeedback = 2 SyncPortA = 3 SyncPortB = 4 end |
| enum CammingOutput
RelativePosition = 1 AbsolutePosition = 2 Velocity = 3 end |
Disables camming on the specified follower axis.
Arguments
$followerAxis The follower axis on which to disable camming.
Unloads a camming table from the SMC.
Arguments
$tableNum The camming table number to remove. This value must be greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 99.
Gearing Motion
Gearing motion causes a follower axis to follow the position of a leader axis. Use the GearingSetLeaderAxis() function to configure the relation between the follower axis and the leader axis. Set the $gearingSource argument with enum GearingSource. The controller continuously maintains the follower axis velocity in proportion with the leader axis velocity based on a fixed ratio that you set with the GearingSetRatio() function.
IMPORTANT: The ReverseMotionDirection Parameter for the follower axis has no effect on the direction of motion for the follower axis. To reverse the direction of the follower axis relative to the leader axis, use a negative gear ratio.
After you configure the gearing motion, you can enable it with the GearingOn() function. This function has two modes, unfiltered and filtered, which you set with the $filter argument in enum GearingFilter
- Unfiltered: If you enable the gearing motion with unfiltered mode, the controller does not smooth out sudden changes in the velocity of the leader axis.
- Filtered: If you enable the gearing motion with filtered mode, the controller smooths out sudden changes in the velocity of the leader axis to prevent the controller from transmitting them to the follower axis.
To disable gearing motion, use the GearingOff() function.
Configures gearing for an axis.
Arguments
$followerAxis Follower axis for the gearing setup.
$leaderAxis Leader axis for the gearing setup.
$gearingSource Input data source for gearing.
| enum GearingSource
PositionFeedback = 0 PositionCommand = 1 AuxiliaryFeedback = 2 SyncPortA = 3 SyncPortB = 4 end |
Sets the gearing ratio for an axis.
Arguments
$followerAxis The axis on which to set the gear ratio.
$gearRatio The scale factor applied to the motion of the follower axis, specified as the ratio of follower axis counts to leader axis counts. A negative gear ratio will cause the follower axis to move in the opposite direction of the motion of the leader axis.
Enables gearing on an axis.
Arguments
$followerAxis The axis on which to enable gearing.
$filter Type of filter applied to follower axis motion.
| enum GearingFilter
None = 1 Filtered = 2 end |
Disables gearing on an axis.
Arguments
$followerAxis The axis on which to disable gearing.
Feedback Latency
In Automation1, the communication latency between the drives and the controller can delay the motion of the follower axis. If you configure gearing with a gearing source of PositionFeedback, AuxiliaryFeedback, SyncPortA, or SyncPortB, then a delay of approximately 10 milliseconds will occur between the motion of the leader axis and the corresponding motion of the follower axis. To prevent this delay, set the gearing source to PositionCommand or use the Autofocus feature with auxiliary encoder feedback.
To command gearing motion from encoder feedback with less than a millisecond of delay, use Autofocus with auxiliary encoder feedback. In this mode, the latency between the motion of the leader axis and the motion of the follower axis is equal to 1 divided by the Position Update Rate of the follower axis. For example, if the follower axis is an XC4, then a 0.05-millisecond delay will occur between the motion of the leader axis and the motion of the follower axis. Do the steps that follow to configure gearing with Autofocus:
- Set the AutofocusInput Parameter to AuxiliaryEncoderFeedback.
- Set the AutofocusTarget Parameter to 0.
- Set the AutofocusGainK Parameter to 1 and set all other Autofocus gains to 0.
- Configure the gear ratio by setting the AutofocusEncoderScaleFactor Parameter to the necessary gearing ratio of follower axis counts to leader axis counts.
- Configure the direction of gearing with the Loop Polarity setting in the AutofocusSetup Parameter. A Normal Loop Polarity will cause the follower axis to move in the opposite direction to the encoder input. An Inverted Loop Polarity will cause the follower axis to move in the same direction as the encoder input.
- Use the
AutofocusOn()function with the AutofocusFocusMode.Continuous enum to enable gearing. To get the values of this enum, see AeroScript Enums. To disable gearing, use theAutofocusOff()function.
For more information about how to use the Autofocus feature, see Autofocus Functions.