Sine Wave Encoder (Primary) [-CT1/-CT2/-CT4 Option]
The Sine Wave Encoder option provides higher positioning resolution by subdividing the fundamental output period of the encoder into smaller increments. The amount of subdivision is specified by the PrimaryEncoderMultiplicationFactor parameter. Use Encoder Tuning to adjust the value of the gain, offset, and phase balance controller parameters to get the best performance. For more information, refer to Automation1 Help.
High resolution or high-speed encoders can require increased bandwidth for correct operation. Use the High Speed Mode of the PrimaryEncoderMultiplierSetup parameter to enable the high bandwidth mode. Because this mode increases sensitivity to system noise, use it only if necessary.
The iXR3/XR3 with the -CT2 and -CT4 options can generate emulated encoder signals. These signals can be output on the AUX ENCODER connector, the HSOUT (High-Speed Output) connector, or used internally by the PSO. Refer to the PrimaryEmulatedQuadratureDivider parameter and the encoder output functions in Automation1 Help for more information.
You cannot use a sine wave encoder with the -CT1 multiplier option as an input to the PSO. The -CT1 option does not generate emulated quadrature signals.
For the highest performance, use twisted pair double-shielded cable with the inner shield connected to signal common and the outer shield connected to frame ground. Do not join the inner and outer shields in the cable.
Table 2-13: Sine Wave Encoder Specifications
|
Specification |
Value |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Auxiliary | ||
|
Input Frequency (max) |
450 kHz, 2 MHz |
||
|
Input Amplitude (1) |
0.6 to 1.75 Vpk-pk |
||
|
Interpolation Factor (max) |
-CT1 |
16,384 |
N/A |
|
-CT2 |
65,536 |
N/A |
|
| -CT4 | 65,536 | 65,536 | |
|
-CT2/-CT4 Primary Encoder Channel Interpolation Latency |
800 nsec (analog input to quadrature output) |
||
|
Input Common Mode |
1.5 to 3.5 VDC |
||
|
(1) Measured as SIN(+) - SIN(-) or COS(+) - COS(-) |
|||
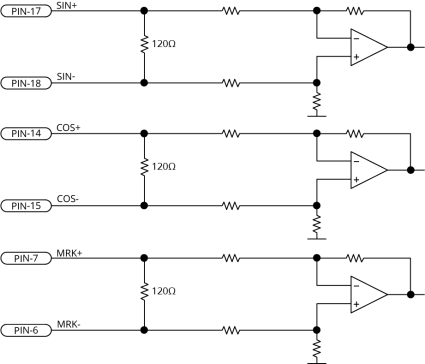
Figure 2-16: Sine Wave Encoder Phasing Reference Diagram
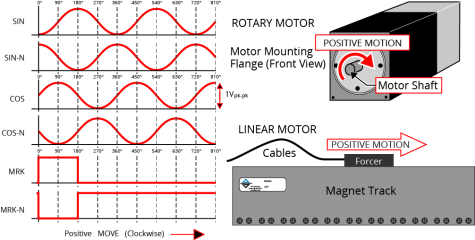
Figure 2-17: Sine Wave Encoder Schematic (Feedback Connector)