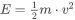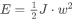Internal Shunt Option [-SI#]
The internal shunt option is used to limit the internal bus voltage caused by regeneration. Regeneration occurs during deceleration as mechanical energy is converted to electrical energy and stored in the internal power supply capacitors. Regeneration only occurs with PWM amplifier types (XSP3) and not linear amplifier types (XSL3).
The maximum amount of energy that the iXR3/XR3 can safely absorb depends on the line voltage and motor bus configuration as shown in Maximum Energy That The iXR3/XR3 Can Safely Absorb During Regeneration.
Table 2-3: Maximum Energy That The iXR3/XR3 Can Safely Absorb During Regeneration
|
Bus Option |
Input Voltage |
Internal Capacitance |
Energy (J) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
VB7 - with split bus |
125 VAC |
8000 uF / 200 VDC |
35 |
|
VB7 - without split bus |
125 VAC |
16000 uF / 200 VDC |
70 |
|
VB8 - with split bus |
240 VAC |
2300 uF / 400 VDC |
52 |
|
VB8 - without split bus |
240 VAC |
4600 uf / 400 VDC |
104 |
To determine if the shunt option is required, use one of the equations that follow to calculate the stored mechanical energy. If the calculated value exceeds the value listed in Maximum Energy That The iXR3/XR3 Can Safely Absorb During Regeneration, the shunt option is required. For multiple axes, add the energy contribution for each axis that shares a power supply and decelerates simultaneously. Compare the sum against the maximum energy limits shown in Maximum Energy That The iXR3/XR3 Can Safely Absorb During Regeneration.
|
For Linear Axes: |
|
For Rotary Axes: |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
m |
moving mass [kg] |
|
|
J |
inertia [kg·m 2 ] |
|
|
v |
speed [m/s] |
|
|
w |
speed [rad/s] |
|
|
E |
stored energy [J] |
|
|
E |
stored energy [J] |