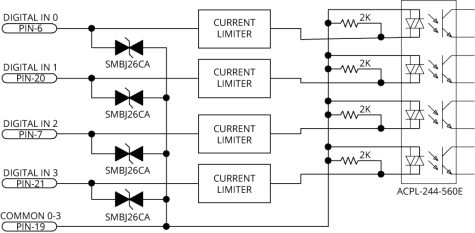
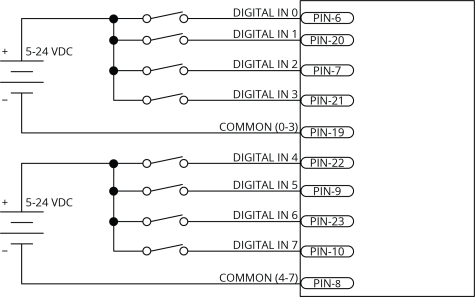
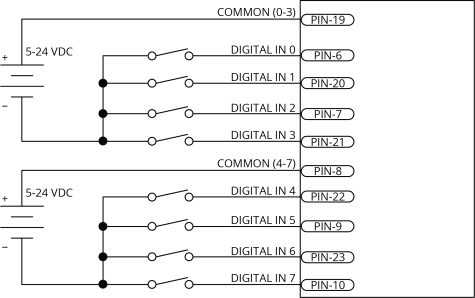
Digital Inputs
Input bits are arranged in groups of 4 and each group shares a common pin. This lets a group be connected to current sourcing or current sinking devices, based on the connection of the common pin in that group.
To be able to connect an input group to current sourcing devices, connect the input group's common pin to the power supply return (-). Refer to Digital Inputs Connected to Current Sourcing (PNP) Devices.
To be able to connect an input group to current sinking devices, connect the input group's common pin to the power supply source (+). Refer to Digital Inputs Connected to Current Sinking (NPN) Devices.
The digital inputs are not designed for high-voltage isolation applications. They should only be used with ground-referenced circuits.
Table 2-27: Digital Input Specifications
|
Input Voltage |
Approximate Input Current |
Turn On Time |
Turn Off Time |
|---|---|---|---|
|
+5 V to +24 V |
6 mA |
10 µs |
43 µs |
Table 2-28: Digital Input Pins on the Digital I/O Connector
|
Pin # |
Description |
In/Out/Bi |
|---|---|---|
| 19 | Input Common for Digital Inputs 0-3 | Output |
|
6 |
Opto-Isolated Digital Input 0 |
Input |
| 20 | Opto-Isolated Digital Input 1 |
Input |
|
7 |
Opto-Isolated Digital Input 2 |
Input |
| 21 | Opto-Isolated Digital Input 3 |
Input |
|
8 |
Input Common for Digital Inputs 4-7 | Output |
| 22 | Opto-Isolated Digital Input 4 | Input |
| 9 | Opto-Isolated Digital Input 5 | Input |
| 23 | Opto-Isolated Digital Input 6 | Input |
| 10 | Opto-Isolated Digital Input 7 | Input |