Transformer Options (-AC Option)
You can connect an external isolation transformer to the Motor Supply AC Input to reduce the operating voltage of the motor. Using a transformer can also reduce electrical noise.
Table 2-12: Nominal Motor Operating Voltages / Required AC Voltages
| AC Voltage | DC Voltage |
|---|---|
|
28 |
40 |
|
56 |
80 |
|
115 |
160 |
|
230 |
320 |
Table 2-13: Transformer Options
| Transformer | Description |
|---|---|
|
Generate 28 or 56 VAC from 115 VAC or 230 VAC input source voltage. When rectified by the drive, it produces a 40 or 80 VDC power bus. |
|
|
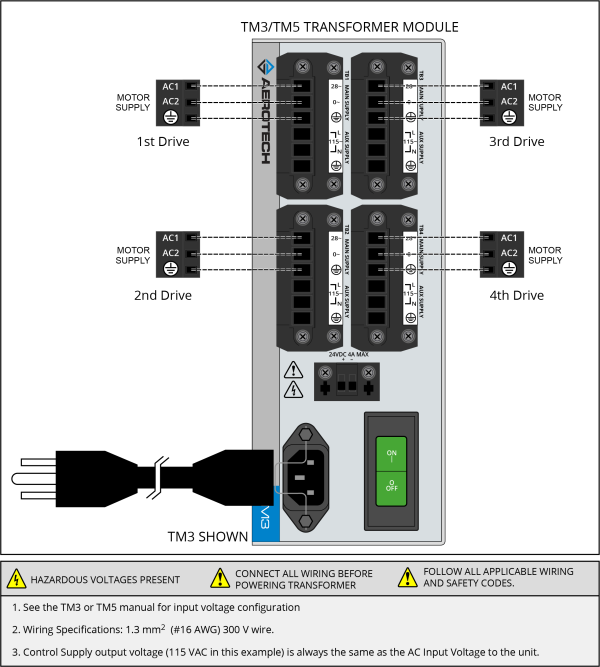
Power up to 4 drives, providing 300 watts of power |
|
|
Power up to 4 drives providing 500 watts of power |
|
|
Generate 28 VAC from 115 VAC or 230 VAC input source voltage. When rectified by the drive, it produces a 40 VDC power bus. |
|
|
Generate 56 VAC from 115 VAC or 230 VAC input source voltage. When rectified by the drive, it produces an 80 VDC power bus. |
|
|
TV1.5, TV2.5, or TV5 |
1.5 kVA, 2.5 kVA, or 5 kVA isolation transformer; 115/230 VAC input; 28, 43, 56, 70, 115 VAC output |
Figure 2-7: TV0.3-28-56-ST Transformer Motor Power Wiring (40 VDC Bus) [
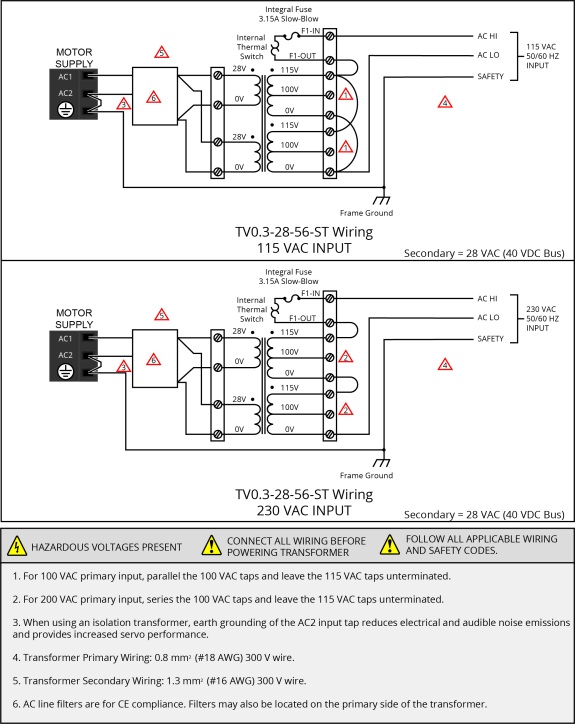
Figure 2-8: TV0.3-28-56-ST Transformer Motor Power Wiring (80 VDC Bus) [
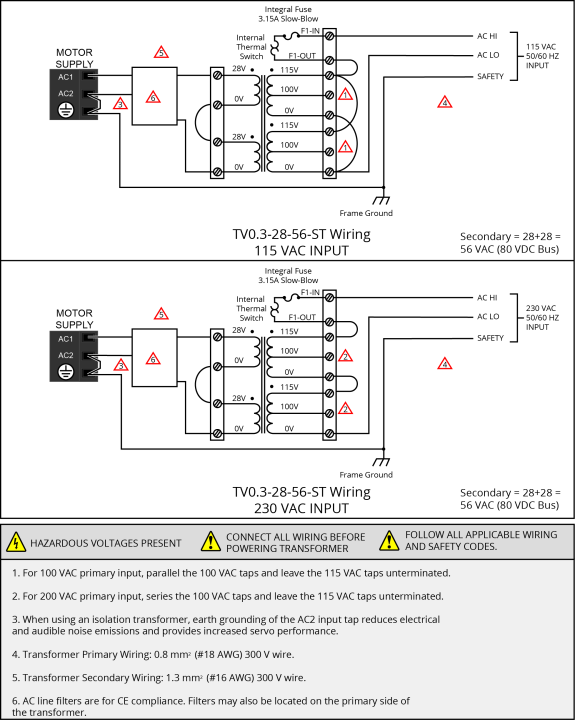
Figure 2-9: TV0.3-28-56-ST Transformer Motor Power Wiring (160 VDC Bus) [
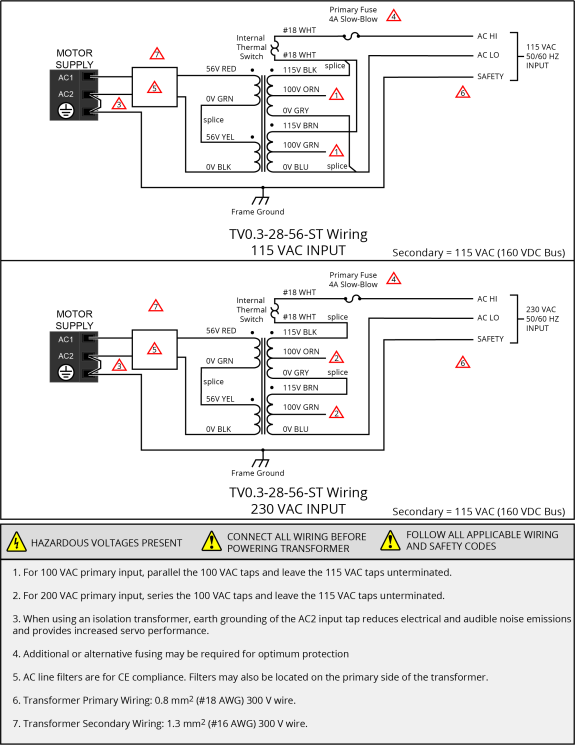
Figure 2-10: TV0.3-28 Transformer Motor Power Wiring (40 VDC Bus) [
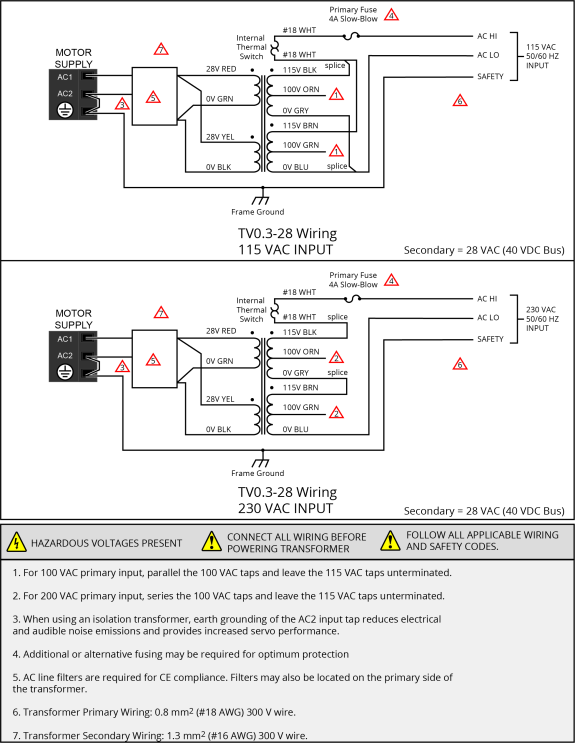
Figure 2-11: TV0.3-56 Transformer Motor Power Wiring (80 VDC Bus) [
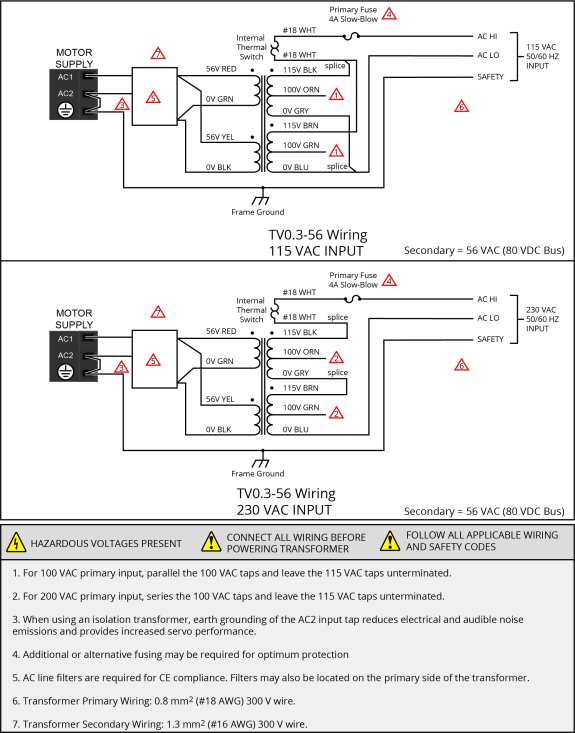
Figure 2-12: TM3/TM5 Transformer Motor Power Wiring [